6 things to know about having a C-section
Surgical deliveries account for about one-third of all births in the United States.
Updated on March 11, 2025

About one in three births in the United States are cesarean deliveries, also called C-sections, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). C-sections occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from the parent’s personal preference to the position of the fetus, to saving the life of both parent and baby.
Here’s what to know about this common surgery, in which delivery occurs via an incision in the abdomen and uterus.
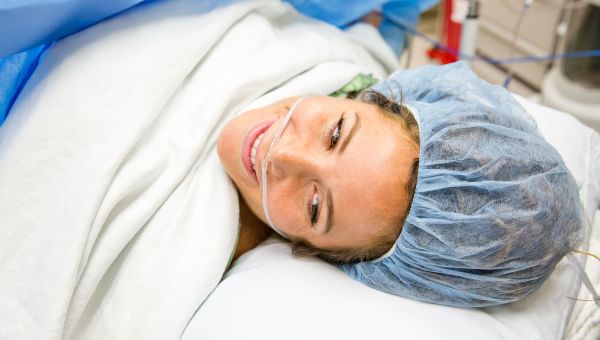
You'll likely be awake during a c-section
If you have a C-section, you will probably be awake and alert during the procedure—though each case is different. Most often, the body is numbed below the waist using regional anesthesia (which affects a part or region of the body), such as an epidural, spinal block, or both.
A spinal block is a one-time injection of a narcotic pain medicine, such as fentanyl, or anesthetic into the spinal fluid. An epidural is also administered in the pregnant person’s back, but it's done using a catheter tube that remains in place, so more anesthetic can be given as needed. Although you shouldn’t feel any pain once you’ve been given the anesthetic, you may feel some pressure.
In the case of an emergency C-section, it may be necessary for the doctor to administer general anesthesia, which brings on a sleep-like state so you won’t feel the pain.
Once anesthesia—local or general—is administered, your surgeon will make an incision on the lower part of your abdomen, through which the baby will be delivered.

C-sections are sometimes safer than vaginal deliveries
Though a patient or surgeon may sometimes schedule a C-section out of personal preference, C-sections are typically performed when a vaginal birth is deemed high-risk. These scenarios may include:
- The fetus is in a breech position, or feet first
- The pregnant person has had previous C-sections
- Twins, triplets, or more are expected
It may also be performed when a pregnant person has:
- Diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels
- Preeclampsia, which is high blood pressure, protein in the urine, vision changes, and fluid retention and can cause serious complications for the parent and fetus
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which weakens the immune system
- An active case of genital herpes, a viral infection that causes sores
Complications during an attempted vaginal delivery can also lead to an emergency C-section. "Common reasons for an unplanned cesarean section include excessive bleeding during vaginal delivery, cord [entanglement, when umbilical cord loops around a part of the fetus] or placental abruption [separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus]," according to Reut Bardach, MD, an OBGYN in Trinity, Florida.
C-sections may also be performed if labor does not progress or the fetus’s heartrate is slow, a sign of distress.
There are some risks to C-sections
Most obstetricians perform hundreds or thousands of these surgeries, making them routine. But like any major surgery, C-sections do come with some risks. "Although it definitely poses some risk of complication, most surgeons are very comfortable and confident performing C-sections, so they generally run smoothly," Bardach says.
"The first risk in an abdominal surgery, and especially in C-sections, is bleeding," Bardach says. "By the mere fact that we're using scalpels, there's going to be some blood loss involved."
There are some other risks to the pregnant person, including infection, damage to surrounding organs, and blood clots. Although unlikely, it's possible for the baby to have surgery-related injuries, such as small cuts. Babies born via C-section are also at an increased risk of developing a breathing issue known as transient tachypnea, in which the baby experiences rapid breathing in the days following delivery.
But in general, cesarean deliveries pose a very low risk to parent and child. "My personal philosophy is that having a vaginal delivery is safer," Bardach says. "Our bodies are designed to have babies vaginally, but both options have their own benefits."
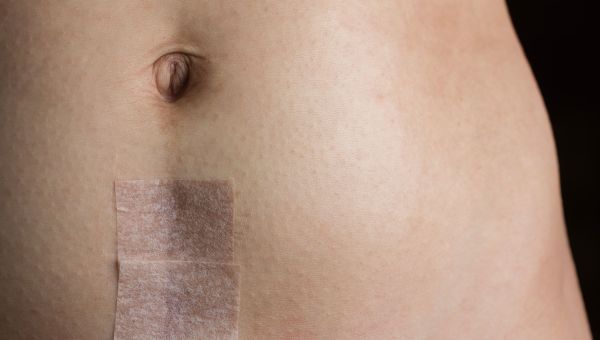
The type of scar will depend on your surgery
As with any surgery that involves incisions, a C-section will leave you with a scar, though the placement depends on many factors, such as the position of the fetus. The most common type of incision is called a "bikini incision" and it is done horizontally, just above the pubic hairline, in an area often covered by a swimsuit or underwear. In some cases, mainly when a large incision is needed or the baby must be removed quickly, the surgeon may make a vertical incision just below the belly button. A vertical incision can also be made higher up, particularly if the fetus is lying sideways in the uterus.
Whether the first incision is vertical or horizontal, a second incision is then made in the uterine wall, and the baby is delivered through these two openings. If you’ve had a C-section in the past, that will also help your surgeon determine where to make the new incision.
Regardless of the position of the incision, it is usually around 4 to 6 inches long, big enough for the baby’s head and body to squeeze through.
Your medical team will give you instructions for how to care for the incision after surgery, and the amount of scarring can depend on many things, including genetics. Over time, the scar will fade and become smaller. If it bothers you, there are several treatment options to help minimize the appearance, including creams, injections, and laser therapy.

Vaginal birth after a C-section is possible
Just because you had a C-section for one delivery does not necessarily mean you will need to have another C-section if you have more children in the future. In 2020, about 16.2 percent of people who gave birth vaginally in the U.S. had a previous C-section, according to a 2023 analysis in Obstetrics and Gynecology. This is called vaginal birth after cesarean delivery (VBAC).
If you’re interested in attempting a VBAC, discuss the risks with your doctor—your chance of success depends on the reasons you had the C-section in the first place and if there were any complications. It may also depend on the type of incision you had. People with a prior vertical incision to the uterus are more likely to need a second cesarean. C-sections increase the risk for placental complications, which might lead to an additional procedure.

You'll need help during recovery
Recovering from a C-section takes time and rest. It is, after all, major abdominal surgery. "Postoperatively a lot of people need assistance, and having supportive family and friends is a huge benefit," Bardach says.
It generally takes longer to recover from a C-section than a vaginal delivery, and you will likely stay in the hospital one or two days longer. For days, and even weeks, after the procedure, you might feel tired, sore near the incision, constipated or full of gas, and you may have difficulty getting out of bed or lifting your baby.
To help with healing, rest when possible, drink plenty of fluids, avoid sex until your doctor gives you the okay (usually at your six-week checkup), and take medication as recommended to manage pain when needed. Walking as you are able may also relieve discomfort and help prevent blood clots. Using a pillow to support your abdomen when you sneeze, cough, or laugh may be helpful to relieve pressure in this area, as well. Most people are back to their typical activities between six and eight weeks after delivery.
There are no restrictions on breastfeeding, and you can begin as soon as you feel up to it. If you’re uncomfortable breastfeeding because of your incision, feel pain while nursing, or have issues with milk supply, ask a nurse, doula (a professional trained to support a parent before, during, and after childbirth), or lactation consultant to help you find solutions. If you have questions about support during recovery and breastfeeding and whether your insurance covers, ask your HCP.
Taking care of yourself is crucial at this time, and if you decide that breastfeeding isn’t right for you as you recover, supplementing or bottle feeding are healthy options.

Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics: Method of Delivery. April 9, 2024.
Mayo Clinic. C-section. June 16, 2022.
Nemours Kids Health. Cesarean Sections (C-Sections). June 2022.
Mayo Clinic. General anesthesia. January 17, 2025.
MedlinePlus. Cesarean Delivery. April 20, 2023.
Cleveland Clinic. C-Section. August 14, 2022.
Merck Manual Consumer Version. Cesarean Delivery. March 2024.
American Academy of Dermatology Association. Keloid Scares: Overview. Last updated August 30, 2022.
Mayo Clinic. Uterine incisions used during C-sections. Accessed September 18, 2023.
Osterman MJK. Recent Trends in Vaginal Birth After Cesarean Delivery: United States, 2016-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020 Mar;(359):1-8.
Bruno AM, Allshouse AA, Metz TD. Trends in Attempted and Successful Trial of Labor After Cesarean Delivery in the United States From 2010 to 2020. Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Jan 1;141(1):173-175.
More On


video

article

slideshow


video


video
